

Next: About this document ...
Up: Evolution of Complexity in
Previous: The Reality Effect
- 1
-
20th Century Fox (1966) Fantastic Voyage.
R. Fleischer, director (Film).
- 2
-
Ahuja, R. K., Magnanti, T. L. and Orlin, J. B. (1993) Network Flows.
Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs.
- 3
-
Ali, A., Helgason, R. V., Kennington, J. L. and Lall, H. (1980) Computational
comparison among three multicommodity network flow algorithms.
Operations Research 28: 995-1000.
- 4
-
Angeline, P. J. and Pollack, J. B. (1993) Competitive environments evolve
better solutions for complex tasks.
Forrest, S. (ed.), Proceedings of the Fifth International
Conference on Genetic Algorithms. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, Calif.,
264-270.
- 5
-
Angeline, P. J. and Pollack, J. B. (1994) Coevolving high-level
representations.
Artificial life III. Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass., 55-71.
- 6
-
Axelrod, R. (1987) The evolution of strategies in the iterated prisoner's
dilemma.
Davis, L. (ed.), Genetic Algorithms and Simulated Annealing,
Pitman: London.
- 7
-
Baxter, J., Tridgell, A. and L.Weaver (1998) TDLeaf(
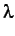 ): Combining
temporal difference learning with game-tree search.
): Combining
temporal difference learning with game-tree search.
Proceedings of the Ninth Australian Conference on Neural
Networks. 168-172.
- 8
-
Beasley, D., Bull, D. R. and Martin, R. R. (1993) A sequential niche technique
for multimodal function optimization.
Evolutionary Computation 1(2): 101-125.
- 9
-
Belew, R. K., McInerney, J. and Schraudolf, N. (1990) Evolving networks, using
the genetic algorithm with connectionist learning.
Technical Report CSE-CS-174, UCSD.
- 10
-
Bennet, C. H. (1985) Emerging Syntheses in Science.
Pines.
- 11
-
Bentley, P. (ed.) (1999) Evolutionary Design by Computers.
Morgan-Kaufmann, San Francisco.
- 12
-
Bentley, P. J. (1996) Generic Evolutionary Design of Solid Objects using a
Genetic Algorithm.
Ph.D. thesis, Division of Computing and Control Systems, School of
Engineering, The University of Huddersfield.
- 13
-
Bezerra, C. and Owen, C. L. (2000) Evolutionary structured planning.
Gero, J. S. (ed.), Artificial Intelligence in Design '00.
Kluwer Academic, 287-307.
- 14
-
Brooks, R. (1991) Intelligence without reason.
Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on
Artificial Intelligence. IJCAI, San Mateo, Calif., 569-595.
- 15
-
Brooks, R. (1991) Intelligence without representation.
Artificial Intelligence 47(1-3): 139-160.
- 16
-
Brooks, R. A. (1986) A robust layered control system for a mobile robot.
IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation 2(1): 14-23.
- 17
-
Carroll, S. B. (2000) Endless forms: The evolution of gene regulation and
morphological diversity.
Cell 101: 577-580.
- 18
-
Castro, J. and Nabona, N. (1996) An implementation of linear and nonlinear
multicommodity network flows.
European Journal of Operational Research 92: 37-53.
- 19
-
Chaitin, G. J. (1966) On the length of programs for computing finite binary
sequences.
Journal of the ACM 13(4): 547-569.
- 20
-
Chapman, C. D., Saitou, K. and Jakiela, M. J. (1993) Genetic algorithms as an
approach to configuration and topology design.
Gilmore, B. (ed.), Advances in Design Automation. American
Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), New York, no. 65:1 in series DE,
485-498.
- 21
-
Cherkassky, B. V. and Goldberg, A. V. (1997) On implementing push-relabel
method for the maximum flow problem.
Algorithmica 19: 390-410.
- 22
-
Cliff, D., Harvey, I. and Husbands, P. (1993) Explorations in evolutionary
robotics.
Adaptive Behavior 2(1): 71-108.
- 23
-
Cliff, D., Husbands, P. and Harvey, I. (1992) Analysis of evolved sensory-motor
controllers.
Technical Report Technical Report CSRP 264, University of Sussex
School of Cognitive and Computing Sciences.
- 24
-
Cliff, D. and Miller, G. (1995) Tracking the Red Queen: Measurements of
adaptive progress in co-evolutionary simulations.
Morán, F., Moreno, A., Merelo, J. J. and Chacón, P. (eds.), Advances in Artificial Life: Third European Conference on Artificial
Life. Springer, Berlin, New York, no. 929 in Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, 200-218.
- 25
-
Cliff, D. and Miller, G. (1996) Co-evolution of pursuit and evasion II:
Simulation methods and results.
From Animals to Animats 4. MIT Press, 506-515.
- 26
-
Cliff, D. and Noble, J. (1997) Knowledge-based vision and simple visual
machines.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London:
Series B 352: 1165-1175.
- 27
-
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. and Rivest, R. L. (1989) Introduction to
Algorithms.
MIT Press - McGraw Hill.
- 28
-
Cziko, G. (1995) Without Miracles: Universal Selection Theory and the
Second Darwinian Revolution.
MIT Press, Cambridge, USA.
- 29
-
Dawkins, R. (1983) Universal darwinism.
Bendall, D. S. (ed.), Evolution from Molecules to Man,
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 403-425.
- 30
-
Dawkins, R. (1987) The Blind Watchmaker.
W. W. Norton, New York.
- 31
-
Dawkins, R. (1996) Climbing Mount Improbable.
W. W. Norton, New York.
- 32
-
Di Paolo, E. A. (2000) Homeostatic adaptation to inversion of the visual
field and other sensorimotor disruptions.
Meyer, J., Berthoz, A., Floreano, D., Roitblat, H. and Wilson, S. W.
(eds.), From Animals to Animats 6. MIT Press, Cambridge (Mass),
London (England), 440-449.
- 33
-
Edmonds, B. (1999) Syntactic Measures of Complexity.
Ph.D. thesis, University of Manchester, Department of Philosophy.
- 34
-
Elo, A. E. (1986) The Rating of Chessplayers, Past and Present.
Arco Pub., New York, 2nd ed.
- 35
-
Fahlman, S. E. (1974) A planning system for robot construction tasks.
Artificial Intelligence 5: 1-49.
- 36
-
Floreano, D. (1998) Evolutionary robotics in artificial life and behavior
engineering.
Gomi, T. (ed.), Evolutionary Robotics, AAI Books, Ontario
(Canada).
- 37
-
Floreano, D. and Mondada, F. (1994) Automatic creation of an autonomous agent:
Genetic evolution of a neural network driven robot.
D. Cliff, P. H., Meyer, J. and Wilson, S. W. (eds.), From
Animals to Animats 3. MIT Press, Bradford Books.
- 38
-
Floreano, D. and Mondada, F. (1996) Evolution of homing navigation in a real
mobile robot.
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics .
- 39
-
Floreano, D., Nolfi, S. and Mondada, F. (1998) Competitive co-evolutionary
robotics: From theory to practice.
From Animals to Animats 4. MIT Press.
- 40
-
Fogel, D. B. (2000) Evolving a checkers player without relying on human
expertise.
Intelligence 11(2): 20-27.
- 41
-
Forbus, K. (1984) Qualitative process theory.
Artificial Intelligence 24: 85-168.
- 42
-
Fukuda, T. and Kawauchi, Y. (1990) Cellular robotic system (CEBOT) as one of
the realization of self-organizing intelligent universal manipulator.
Proceedings of the 1990 IEEE International Conference on
Robotics and Automation. 662-667.
- 43
-
Funes, P. (1996) The Tron game: an experiment in artificial life and
evolutionary techniques.
(Unpublished).
- 44
-
Funes, P. (2000) Measuring progress in coevolutionary competition.
Meyer, J., Berthoz, A., Floreano, D., Roitblat, H. and Wilson, S. W.
(eds.), From Animals to Animats 6. MIT Press, Cambridge (Mass),
London (England), 450-459.
- 45
-
Funes, P., Lapat, L. B. and Pollack, J. B. (2000) EvoCAD: Evolution-assisted
design.
Artificial Intelligence in Design'00 (Poster Abstracts). Key
Centre of Design Computing and Cognition, University of Sidney, 21-24.
- 46
-
Funes, P. and Pollack, J. B. (1997) Computer evolution of buildable objects.
Husbands, P. and Harvey, I. (eds.), Fourth European Conference
on Artificial Life. MIT Press, Cambridge, 358-367.
- 47
-
Funes, P. and Pollack, J. B. (1998) Componential structural simulator.
Technical Report CS-98-198, Brandeis University Department of
Computer Science.
- 48
-
Funes, P. and Pollack, J. B. (1998) Evolutionary body building: Adaptive
physical designs for robots.
Artificial Life 4(4): 337-357.
- 49
-
Funes, P. and Pollack, J. B. (1999) Computer evolution of buildable objects.
Bentley, P. (ed.), Evolutionary Design by Computers,
Morgan-Kaufmann, San Francisco. 387 - 403.
- 50
-
Funes, P., Sklar, E., Juillé, H. and Pollack, J. B. (1998) Animal-animat
coevolution: Using the animal population as fitness function.
From Animals to Animats 5. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA,
University of Zurich, 525-533.
- 51
-
Funes, P., Sklar, E., Juillé, H. and Pollack, J. B. (1998) Animal-animat
coevolution: Using the animal population as fitness function.
Pfeiffer, Blumberg, Wilson and Meyer (eds.), From Animals to
Animats 5. MIT Press.
- 52
-
Gardin, F. and Meltzer, B. (1989) Analogical representations of naive physics.
Artificial Intelligence 38: 139-159.
- 53
-
Gell-Mann, M. and Lloyd, S. (1996) Information measures, effective complexity,
and total information.
Complexity 2(1): 44-52.
- 54
-
Glickman, M. E. (1999) Parameter estimation in large dynamic paired comparison
experiments.
Applied Statistics 48: 377-394.
- 55
-
Goldberg, D. (1989) Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and
Machine Learning.
Addison-Wesley, Reading.
- 56
-
Gould, S. and Vrba, E. (1982) Exaptation - a missing term in the science of
form.
Paleobiology 8: 4-15.
- 57
-
Gould, S. J. (1996) Full house: the spread of excellence from Plato to
Darwin..
Harmony Books, New York.
- 58
-
Grassberger, P. (1990) Information and complexity measures in dynamical
systems.
Information Dynamics. Plenum Press, New York.
- 59
-
Grigoriadis, M. D. and Khachiyan, L. G. (1995) An exponential-function
reduction method for block-angular convex programs.
Networks 26: 59-68.
- 60
-
Gruau, F. (1992) Cellular encoding of genetic neural networks.
Technical Report 92.21, Laboratoire de l'Informatique du
Parallélisme, Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon.
- 61
-
Gruau, F. (1993) Genetic synthesis of modular neural networks.
Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Genetic
Algorithms. Morgan-Kaufman, 318-325.
- 62
-
Harvey, I. (1997) Artificial evolution for real problems.
Gomi, T. (ed.), Evolutionary Robotics: From Intelligent Robots
to Artificial Life (ER'97). AAI Books, Kanata, Ontario Canada, 127-149.
- 63
-
Heylighen, F. (1989) Self-organization, emergence and the architecture of
complexity.
Proceedings of the First European Conference on System
Science. AFCET, Paris, 23-32.
- 64
-
Heylighen, F. (1999) The growth of structural and functional complexity during
evolution.
Heylighen, F., Bollen, J. and Riegler, A. (eds.), The Evolution
of Complexity, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht-Boston-London. 17-43.
- 65
-
Hillis, D. (1991) Co-evolving parasites improves simulated evolution as an
optimization procedure.
C. Langton, C. Taylor, J. F. and Rasmussen, S. (eds.), Artificial Life II, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
- 66
-
Hornby, G. S., Lipson, H. and Pollack, J. B. (2001) Evolution of generative
design systems for modular physical robots.
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
(to appear).
- 67
-
Husbands, P. and Harvey, I. (1992) Evolution versus design: Controlling
autonomous robots.
Proceedings of the Third Annual Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, Simulation and Planning. IEEE Press, 139-146.
- 68
-
Iusem, A. and Zenios, S. (1995) Interval underrelaxed Bregman's method with
an application.
Optimization 35(3): 227.
- 69
-
Jacobs, R. A., Jordan, M. I., Nowlan, S. J. and Hinton, G. E. (1991) Adaptive
mixtures of local experts.
Neural Computation 3: 79-87.
- 70
-
Jakobi, N. (1994) Evolving sensorimotor control architectures in simulation for
a real robot.
Master's thesis.
- 71
-
Jakobi, N. (1997) Half-baked, ad hoc, and noisy: minimal simulations for
evolutionary robotics.
Husbands, P. and Harvey, I. (eds.), Fourth European Conference
on Artificial Life. MIT Press, 348-357.
- 72
-
Jakobi, N., Husbands, P. and Harvey, I. (1995) Noise and the reality gap: The
use of simulation in evolutionary robotics.
Morán, F., Moreno, A., Merelo, J. J. and Chacón, P. (eds.), Advances in Artificial Life: Third European Conference on Artificial
Life. Springer, Berlin, New York, no. 929 in Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, 704-720.
- 73
-
Joe, H. (1990) Extended use of paired comparison models, with application to
chess rankings.
Applied Statistics 39(1): 85-93.
- 74
-
Juillé, H. and Pollack, J. B. (1996) Co-evolving intertwined spirals.
Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Genetic
Algorithms. 351-358.
- 75
-
Juillé, H. and Pollack, J. B. (1996) Dynamics of co-evolutionary learning.
From Animals to Animats 4. MIT Press, 526-534.
- 76
-
Kawauchi, Y., Inaba, M. and Fukuda, T. (1999) Genetic evolution and
self-organization of cellular robotic system.
JSME Int. J. Series C. (Dynamics, Control, Robotics, Design &
Manufacturing) 38(3): 501-509.
- 77
-
Keirsey, D. M. (1999) Involution: On the structure and process of existence.
Heylighen, F., Bollen, J. and Riegler, A. (eds.), The Evolution
of Complexity, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht-Boston-London. 45-57.
- 78
-
Kitano, H. (1990) Designing neural network using genetic algorithm with graph
generation system.
Complex Systems 4: 461-476.
- 79
-
Kolmogorov, A. N. (1965) Three approaches to the quantitative definition of
information.
Problems of Information Transmission 1(1): 1-11.
- 80
-
Kolmogorov, A. N. (1983) Combinatorial basis of information theory and
probability theory.
Russian Mathematical Surveys 38: 29-40.
- 81
-
Komosinski, M. and Ulatowski, S. (1999) Framsticks: towards a simulation of a
nature-like world, creatures and evolution.
Floreano, D., Nicoud, J.-D. and Mondada, F. (eds.), Advances in
Artificial Life: 5th European Conference on Artificial Life.
Springer-Verlag, vol. 1674 of Lecture Notes in Artificial
Intelligence, 261-265.
- 82
-
Koppel, M. (1987) Complexity, depth, and sophistication.
Complex Systems 1: 1087-1091.
- 83
-
Kotay, K., Rus, D., Vona, M. and McGray, C. (1998) The self-reconfiguring
robotic molecule.
1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and
Automation,. Robotics and Automation Society.
- 84
-
Koza, J. (1992) Genetic Programming.
MIT Press, Cambridge.
- 85
-
Koza, J. R. (1990) Evolution of subsumption using genetic programming.
Varela, F. J. and Bourgine, P. (eds.), Toward a practice of
autonomous systems: First European Conference on Artificial Life. MIT
Press, 110-119.
- 86
-
K.Sims (1991) Artificial evolution for computer graphics.
Computer Graphics (Siggraph '91 proceedings). 319-328.
- 87
-
Langton, C. (1989) Artificial life.
Langton, C. (ed.), Artificial Life: the proceedings of an
Interdisciplinary Workshop. Addison-Wesley, 1-47.
- 88
-
Lee, W., Hallam, J. and Lund, H. (1996) A hybrid GP/GA approach for
co-evolving controllers and robot bodies to achieve fitness-specified tasks.
Proceedings of IEEE 3rd International Conference on Evolutionary
Computation. IEEE Press, Piscataway, N.J., 384-389.
- 89
-
Leighton, T., Makedon, F., Plotkin, S., Stein, C., Tardos, E. and Tragoudas, S.
(1995) Fast approximation algorithms for muticommodity flow problems.
Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences 50: 228-243.
- 90
-
Lenat, D. and Brown, J. (1984) Why AM and EURISKO appear to work.
Artificial Intelligence 23: 269-294.
- 91
-
Lenat, D. B. (1977) The ubiquity of discovery.
International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (5th,
1977). IJCAI, 1093-1105.
- 92
-
Lewontin, R. C. (2000) The triple helix : gene, organism, and
environment.
Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass.
- 93
-
Lieberman, H. (1997) Autonomous interface agents.
ACM Conference on Human-Computer Interface.
- 94
-
Lipson, H. and Pollack, J. B. (2000) Automatic design and manufacture of
robotic lifeforms.
Nature 406(6799): 974-978.
- 95
-
Lund, H. (1995) Evolving robot control systems.
Alander, J. T. (ed.), Proceedings of the First Nordic Workshop
on Genetic Algorithms and their Applications. University of Vaasa, Vaasa.
- 96
-
Lund, H., Hallam, J. and Lee, W. (1997) Evolving robot morphology.
Proceedings of IEEE Fourth International Conference on
Evolution. IEEE Press.
- 97
-
Margulis, L. (1993) Symbiosis in cell evolution: microbial communities in
the Archean and Proterozoic eons.
Freeman, New York, 2nd ed.
- 98
-
Mataric, M. J. and Cliff, D. (1996) Challenges in evolving controllers for
physical robots.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems 19(1): 67-83.
- 99
-
Maynard Smith, J. and Szathmáry, E. (1997) The major transitions in
evolution.
Oxford University Press, Oxford.
- 100
-
McCabe, T. J. (1976) A complexity measure.
IEEE Transacions on Software Engineering 2(4):
308-320.
- 101
-
Miller, G. F. and Cliff, D. (1994) Protean behavior in dynamic games.
Cliff, D., Husbands, P., Meyer, J. and Wilson, S. (eds.), From
Animals to Animats 3, MIT Press.
- 102
-
Minsky, M. (1986) The Society of Mind.
Simon & Schuster, New York.
- 103
-
Newborn, M. (1996) Kasparov vs. Deep Blue: Computer Chess Comes of Age.
Springer Verlag, New York.
- 104
-
Pamecha, A., Chiang, C., Stein, D. and Chirikjian, G. S. (1996) Design and
implementation of metamorphic robots.
Proceedings of the 1996 ASME Design Engineering Technical
Conference and Computers in Engineering Conference.
- 105
-
Park, H. S. and Gero, J. S. (2000) Categorisation of shapes using shape
features.
Gero, J. S. (ed.), Artificial Intelligence in Design '00.
Kluwer Academic, 203-223.
- 106
-
Plotkin, H. C. (1993) Darwin Machines and the Nature of Knowledge.
Harvard University Press.
- 107
-
Pollack, J. B. and Blair, A. (1997) Why did TD-Gammon work?
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 9:
10-16.
- 108
-
Pollack, J. B., Blair, A. and Land, M. (1996) Coevolution of a backgammon
player.
Langton, C. (ed.), Artificial Life V. MIT Press.
- 109
-
Pollack, J. B. and Blair, A. D. (1998) Coevolution in the successful learning
of backgammon strategy.
Machine Learning 32: 225-240.
- 110
-
Pollack, J. B., Lipson, H., Ficici, S., Funes, P., Hornby, G. and Watson, R.
(2000) Evolutionary techniques in physical robotics.
Miller, J. (ed.), Evolvable Systems: from biology to
hardware. Springer-Verlag, no. 1801 in Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
175-186.
- 111
-
Pollack, J. B., Lipson, H., Funes, P., Ficici, S. G. and Hornby, G. (1999)
Coevolutionary robotics.
Koza, J. R., Stoica, A., Keymeulen, D. and Lohn, J. (eds.), The
First NASA/DoD Workshop on Evolvable Hardware. IEEE Press.
- 112
-
Ray, T. (1992) An approach to the synthesis of life.
C. Langton, C. Taylor, J. F. and Rasmussen, S. (eds.), Artificial Life II, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
- 113
-
Ray, T. S. (1994) An evolutionary approach to synthetic biology: Zen and the
art of creating life.
Artificial Life 1: 179-209.
- 114
-
Reynolds, C. (1994) Competition, coevolution, and the game of tag.
Artificial Life IV, MIT Press. 59-69.
- 115
-
Rich, E. and Kight, K. (1991) Artificial Intelligence.
McGraw-Hill, New York, 2nd ed.
- 116
-
Ronald, E. M. A. and Sipper, M. (2000) Engineering, emergent engineering, and
artificial life: Unsurprise, unsurprising surprise, and surprising surprise.
, M. A. B., McCaskill, J. S., Packard, N. H. and Rasmussen, S.
(eds.), Artificial Life VII. MIT Press, Cambridge, 523-528.
- 117
-
Rosca, J. (1996) Generality versus size in genetic programming.
Proceedings of the Genetic Programming 1996 Conference. MIT
Press.
- 118
-
Rosin, C. D. (1997) Coevolutionary Search Among Adversaries.
Ph.D. thesis, University of California, San Diego.
- 119
-
Rosin, C. D. and Belew, R. K. (1995) Methods for competitive co-evolution:
finding opponents worth beating.
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Genetic
Algorithms. Morgan Kaufman, 373-380.
- 120
-
Schoenauer, M. (1996) Shape representations and evolution schemes.
Fogel, L. J., Angeline, P. J. and Back, T. (eds.), Proceedings
of the 5th Annual Conference on Evolutionary Programming. MIT Press.
- 121
-
Shannon, C. E. (1948) A mathematical theory of communication.
Bell System Technical Journal 27: 379-423,623-656.
- 122
-
Simon, H. A. (1962) The architechture of complexity.
Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 106:
467-482.
- 123
-
Sims, K. (1994) Evolving 3D morphology and behavior by competition.
Brooks, R. and Maes, P. (eds.), Artificial Life IV. MIT
Press, 28-39.
- 124
-
Sims, K. (1994) Evolving virtual creatures.
Computer Graphics, Annual Conference Series.
- 125
-
Sklar, E., Blair, A. D., Funes, P. and Pollack, J. B. (1999) Training
intelligent agents using human internet data.
Liu, J. and Zhong, N. (eds.), Intelligent agent technology:
systems, methodologies, and tools. World Scientific, Singapore, River
Edge, NJ.
- 126
-
Sklar, E. and Pollack, J. B. (2000) A framework for enabling an internet
learning community.
Educational Technology and Society 3(3): 393-408.
- 127
-
Solomonoff, R. J. (1964) A formal theory of inductive inference I, II.
Information Control 7: 1-22, 224-254.
- 128
-
Sutton, R. (1988) Learning to predict by the methods of temporal differences.
Machine Learning 3: 9-44.
- 129
-
Temperley, H. N. (1981) Graph Theory and Applications.
Ellis Horwood, Chichester.
- 130
-
Tesauro, G. (1990) Neurogammon wins computer olympiad.
Neural Computation 1: 321-323.
- 131
-
Tesauro, G. (1992) Practical issues in temporal difference learning.
Machine Learning 8: 257-277.
- 132
-
Tesauro, G. (1995) Temporal difference learning and TD-Gammon.
Communications of the ACM 38(3): 58-68.
- 133
-
Thompson, A. (1995) Evolving electronic robot controllers that exploit hardware
resources.
Morán, F., Moreno, A., Merelo, J. J. and Chacón, P. (eds.), Advances in Artificial Life: Third European Conference on Artificial
Life. Springer, Berlin, New York, no. 929 in Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, 640-656.
- 134
-
Thompson, A. (1998) Hardware evolution : Automatic design of electronic
circuits in reconfigurable hardware by Artificial Evolution.
Springer, London; New York.
- 135
-
Toulmin, S. (1953) The Philosophy of Science.
Hutchinson, London.
- 136
-
V'yugin, V. V. (1999) Algorithmic complexity and stochastic properties of
finite binary sequences.
Computer Journal 42(4): 294-317.
- 137
-
Walt Disney Studios (1982) Tron.
S. Lisberger, director (Film).
- 138
-
Watson, R. A. and Pollack, J. B. (2000) Symbiotic combination as an alternative
to sexual recombination in genetic algorithms.
Schoenauer, M., Deb, K., Rudolph, G., Yao, X., Lutton, E., Merelo,
J. J. and Schwefel, H.-P. (eds.), Proceedings of Parallel Problem
Solving from Nature VI. Springer Verlag, no. 1917 in Lecture Notes in
Computer Science.
- 139
-
Yim, M. (1995) Locomotion With A Unit-Modular Reconfigurable Robot.
Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University, Department of Computer Science.
- 140
-
Yim, M., Duff, D. G. and Roufas, K. D. (2000) PolyBot: a modular
reconfigurable robot.
Proceedings : 2000 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and
Automation. Robotics and Automation Society, Piscataway, NJ.
- 141
-
Zienkiewicz, O. (1977) The Finite Element Method in Engineering
Science.
McGraw-Hill, New York, 3rd ed.
Pablo Funes
2001-05-08